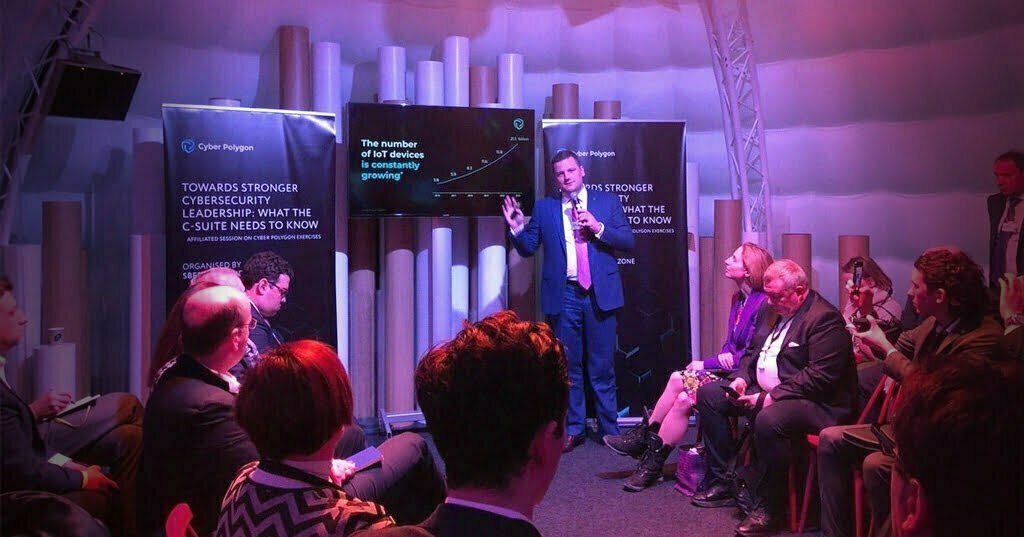
On Wednesday, the World Economic Forum (WEF), along with Russia’s Sberbank and its cybersecurity subsidiary BI.ZONE announced that a new global cyberattack simulation would take place this coming July to instruct participants in “developing secure ecosystems” by simulating a supply-chain cyberattack similar to the recent SolarWinds hack that would “assess the cyber resilience” of the exercise’s participants. On the newly updated event website, the simulation, called Cyber Polygon 2021, ominously warns that, given the digitalization trends largely spurred by the COVID-19 crisis, “a single vulnerable link is enough to bring down the entire system, just like the domino effect,” adding that “a secure approach to digital development today will determine the future of humanity for decades to come.”
The exercise comes several months after the WEF, the “international organization for public-private cooperation” that counts the world’s richest elite among its members, formally announced its movement for a Great Reset, which would involve the coordinated transition to a Fourth Industrial Revolution global economy in which human workers become increasingly irrelevant. This revolution, including its biggest proponent, WEF founder Klaus Schwab, has previously presented a major problem for WEF members and member organizations in terms of what will happen to the masses of people left unemployed by the increasing automation and digitalization in the workplace.
New economic systems that are digitally based and either partnered with or run by central banks are a key part of the WEF’s Great Reset, and such systems would be part of the answer to controlling the masses of the recently unemployed. As others have noted, these digital monopolies, not just financial services, would allow those who control them to “turn off” a person’s money and access to services if that individual does not comply with certain laws, mandates and regulations.
The WEF has been actively promoting and creating such systems and has most recently taken to calling its preferred model “stakeholder capitalism.” Though advertised as a more «inclusive” form of capitalism, stakeholder capitalism would essentially fuse the public and private sectors, creating a system much more like Mussolini’s corporatist style of fascism than anything else.
Yet, to usher in this new and radically different system, the current corrupt system must somehow collapse in its entirety, and its replacement must be successfully marketed to the masses as somehow better than its predecessor. When the world’s most powerful people, such as members of the WEF, desire to make radical changes, crises conveniently emerge—whether a war, a plague, or economic collapse—that enable a “reset” of the system, which is frequently accompanied by a massive upward transfer of wealth.
In recent decades, such events have often been preceded by simulations that come thick and fast before the very event they were meant to “prevent” takes place. Recent examples include the 2020 US election and COVID-19. One of these, Event 201, was cohosted by the World Economic Forum in October 2019 and simulated a novel coronavirus pandemic that spreads around the world and causes major disruptions to the global economy—just a few weeks before the first case of COVID-19 appeared. Cyber Polygon 2021 is merely the latest such simulation, cosponsored by the World Economic Forum. The forum’s current agenda and its past track record of hosting prophetic simulations demands that the exercise be scrutinized.
Though Cyber Polygon 2021 is months off, it was preceded by Cyber Polygon 2020, a similar WEF-sponsored simulation that took place last July in which speakers warned of a coming deadly “pandemic” of cyberattacks that would largely target two economic sectors, healthcare and finance. Cyber Polygon 2020 was officially described as “international online training for raising global cyber resilience” and involved many of the world’s biggest tech companies and international authorities, from IBM to INTERPOL. There were also many surprising participants at the event, some of whom have been traditionally seen as opposed to Western imperial interests. For example, the person chosen to open the Cyber Polygon event was the prime minister of the Russian Federation, Mikhail Mishustin, and its main host, BI.ZONE, was a subsidiary of the Russian-government-controlled Sberbank. This suggests that the overused “Russian hacker” narrative may be coming to an end or will soon be switched out for another boogeyman more suitable in light of current political realities.
Aside from Mishustin, WEF executive director Klaus Schwab and former UK prime minister Tony Blair participated in the Cyber Polygon 2020 event, which is due to be repeated annually and bears many similarities to 2019’s Event 201. Rather than preparing for a potential medical pandemic, Cyber Polygon 2020 focused on preparing for a “cyberpandemic,” one that mainstream media outlets like the New Yorker claim is “already underway.” Given the WEF’s recent simulations, powerful billionaire business owners and bankers appear to be poised to use both physical and digital pandemics to reform our societies according to their own design and for their own benefit.
The Architects of Cyber Polygon
According to Russian cybersecurity firm BI.ZONE, 120 organizations spread over twenty-nine countries took part in the two scenarios that were simulated at Cyber Polygon 2020, with as many as five million people allegedly having watched the livestream in over fifty-seven countries. Like many events that took place in 2020, the Cyber Polygon simulations were conducted online due to COVID-19 restrictions. Together with the World Economic Forum, BI.ZONE, a subsidiary of Sberbank, manages the Cyber Polygon project. Sberbank’s largest shareholder, as of last year, is the Russian government, and it is thus often described by English-language media outlets as a state-controlled bank.
The 2020 event was launched with an address from the prime minister of the Russian Federation Mishustin, who has a history of courting Western tech companies prior to entering politics. In 1989, Mishustin graduated from Moscow State Technological University (generally known as Stankin) with a qualification in systems engineering. During the 1990s, he worked at the International Computer Club, a nonprofit organization with the goal of “attracting Western advanced information technologies” to Russia. Between 1996 and 1998, Mishustin was the chairman of the board of the ICC, but the company was liquidated in 2016. Between 2010 and 2020, he served as head of the Federal Taxation Service of the Russian Federation. Even though he had never shown any previous political ambitions, on January 16, 2020, he was appointed prime minister of the Russian Federation by an executive order issued by President Putin.
During Mishustin’s welcoming remarks at the WEF’s Cyber Polygon 2020, the Russian PM warned of the need to create public policy to “strengthen the digital security of critical activities without undermining the benefits from digital transformation in critical sectors that would unnecessarily restrict the use and openness of digital technology.” The statement suggests that “unnecessary restrictions” could become seen as necessary in time.
Mishustin goes on to explain that Russia’s post-COVID economic recovery will be based on the “increasing digitalization of that economy and government,” adding that “we will drastically increase the number of available digital public services and introduce fundamentally new support measures for digital businesses.” He also stated that “Russia has developed a common national system for identification and the prevention of cyberattacks with the government agency’s information systems linked in the system.” He also addressed the Cyber Polygon audience about the international community needing to come together to prevent a “global cyberfraud pandemic.”
Sberbank, the largest Russian banking institution and former Soviet savings monopoly, which was originally founded by Nicholas I, was an official host of the Cyber Polygon 2020 event alongside the World Economic Forum. As reported in the Economist in January 2021, the Russian banking giant has begun to reimagine its business in an effort to become a consumer-technology giant. Sberbank has spent around $2 billion on technology and acquisitions, including the acquisition of internet media group Rambler, which it fully acquired in 2020. As late as December 30, 2020, Sberbank acquired Doma.ai, which describes itself as “a convenient real estate management platform.” On June 15, 2020, Sberbank bought 2GIS, a map, navigator, and business directory with over 42 million monthly active users. , eleven as the lead investor, include some of the most used services in Russia, and its clear intention is to become a one-stop digital shop for all services. The bank also became the owner of one of the largest data-processing centers in Europe when the South Port data-processing center opened in November 2011, replacing the existing thirty-six regional data centers. Sberbank is set to be the world’s first bank to launch its own cryptocurrency, Sbercoin, and digital finance “ecosystem” this March. It notably announced the coming Sbercoin, a “stablecoin” tied to the Russian ruble, just a few weeks after the Cyber Polygon 2020 exercise.
Sberbank’s alliance with the WEF and prominence at Cyber Polygon 2020 was underscored at the event during the welcoming remarks delivered by Klaus Schwab. Schwab gave special thanks to Herman Gref, a member of the board of trustees of the World Economic Forum and Sberbank’s CEO and also issued the following dire warning:
We all know, but still pay insufficient attention to, the frightening scenario of a comprehensive cyberattack which would bring to a complete halt to the power supply, transportation, hospital services, our society as a whole. The COVID-19 crisis would be seen in this respect as a small disturbance in comparison to a major cyberattack. We have to ask ourselves, in such a situation, how could we let this happen despite the fact we had all the information about the possibility and seriousness of a risk attack. Cybercrime and global cooperation should be on the forefront of the global agenda.
Similar warnings were heard at a 2019 simulation that was also cosponsored by the World Economic Forum, Event 201. Event 201, which simulated a global pandemic just months before the COVID-19 crisis, presciently warned in its official documentation: “The next severe pandemic will not only cause great illness and loss of life but could also trigger major cascading economic and societal consequences that could contribute greatly to global impact and suffering.” In contrast to similar simulations conducted in the past, Event 201 championed a “public-private partnership” approach to combatting pandemics, with a focus on engaging “the private sector in epidemic and outbreak preparedness at the national or regional level.” The WEF is, among other things, a major evangelist for the merging of the public and private sectors globally, describing itself as the “international organization for private-public cooperation.” It is thus unsurprising that their latest disaster simulation, which focuses on cyberattacks, would promote this same agenda.
The Speakers at Cyber Polygon 2020
Aside from Schwab and Mishustin, twenty others took part in Cyber Polygon 2020, including some big names from the top echelons of the political elite. First off, Herman Gref engaged in discussion with former UK prime minister Tony Blair, who has been pushing for digital identity systems for decades. Blair straightforwardly told the CEO of Sberbank that biometric digital identity systems will “inevitably” be the tools that most governments will use to deal with future pandemics. Blair, discussing the coronavirus pandemic with Gref, advocated the harshest of lockdown measures, saying the only alternative to biometric digital identities is to “lockdown the economy.”
Next, Sebastian Tolstoy, Ericsson’s general director for Eastern Europe, Central Asia, and Russia and current chairman of the Tolstoy Family Foundation in Sweden, dialogued with Alexey Kornya. Kornya is president, CEO, and chairman of the management board of Mobile TeleSystems. He previously worked for PricewaterhouseCoopers and AIG-Brunswick Capital Management at North-West Telecom. Tolstoy and Kornya presented a segment at Cyber Polygon 2020 entitled “Building a Secure Interconnected World: What Is the Role of the Telecom Sector?” in which they discussed the importance of digital communication and connectivity to our modern way of living.
In the next segment, Nik Gowing, BBC World News presenter between 1996 and 2014 and founder and director of Thinking the Unthinkable, spoke with Vladimir Pozner, journalist and broadcaster, on the subject of “fake news” in a conversation that was actually somewhat refreshing in its arguments and approach.
Stéphane Duguin, the CEO of the CyberPeace Institute, a Geneva-based company that describes itself as “citizens who seek peace and justice in cyberspace,” then gave a talk to the millions of viewers watching the simulation. The CyberPeace Institute, funded by Microsoft, Facebook, Mastercard, and the Hewlett Foundation, among others, claims to help their customers “increase digital resilience and the capacity to respond to and recover from cyberattacks.” The core backers of the CyberPeace Institute are also among the top backers of the Global Cyber Alliance, which unites the public sectors of the US, UK, and France with multinational corporations and intelligence-linked cybersecurity firms, employing “a coordinated approach and nontraditional collaboration” to “reduce cyber risk.”

Duguin, who is also on the advisory board of the Global Forum on Cyber Expertise, recently launched the Cyber4Healthcare initiative, a “free” cybersecurity service to healthcare providers fighting the COVID-19 pandemic. The Cyber4Healthcare initiative includes as its main partners BI.ZONE as well as Microsoft and the Global Cyber Alliance. This is yet another suspicious Microsoft-linked free cybersecurity service currently being pitched to and adopted by healthcare providers around the world at a time when warnings of a coming cyberattack on healthcare systems globally are becoming more public.
Dhanya Thakkar, senior vice president of AMEA at Trend Micro, who advertises himself online as a top ASEAN LinkedIn “cybersecurity influencer,” and Wendi Whitmore, vice president of IBM X-Force Threat Intelligence, next discussed the topic “Know Your Enemy: How Is the Crisis Changing the Cyberthreat Landscape?” IBM’s presence is notable due to the company’s longstanding relationship with the CIA, dating back to the early Cold War. The company has become so entrenched that the CIA recently recruited their chief information officer directly from IBM Federal. Before joining IBM, Whitmore held executive positions at California-based cybersecurity technology companies CrowdStrike and Mandiant, the latter acquired by FireEye in a stock and cash deal worth in excess of $1 billion. Whitmore was responsible for “professional services.” Notably, both CrowdStrike and Mandiant/FireEye are the key organizations leading the investigation into the recent SolarWinds hack, which US intelligence has blamed on a “Russian hacker” without providing any evidence. Whitmore began her career as a special agent conducting computer crime investigations with the Air Force Office of Special Investigations.
Jacqueline Kernot, the Australian “partner in cybersecurity” for Ernst and Young, and Hector Rodriguez, senior vice president and regional risk officer for Visa, next discussed how to prepare for cyberattacks. Kernot worked for over twenty-five years as a military officer for the Australian Intelligence Corps and spent two years working at IBM’s Defence|Space|Intelligence for Tivoli Software in the UK with “international responsibilities within the UK Ministry of Defence, Defence Primes, and NATO.” Ernst and Young and Visa, alongside other WEF-linked corporations such as Salesforce, are well represented on the Vatican’s exclusive Council for Inclusive Capitalism. The Council, like the WEF, calls for the reconstruction of the economic system to be more “sustainable,” “inclusive,” and “dynamic” by “harnessing the power of the private sector.”
Troels Ørting Jørgensen , chairman of the advisory board of the World Economic Forum’s Centre for Cybersecurity, and Jürgen Stock, the Danish secretary general of INTERPOL, also spoke together at Cyber Polygon regarding the changes in global cybercrime over the course of the previous year. A few months after appearing at Cyber Polygon, the Danish Financial Supervisory Authority announced in an official statement that “Troels Ørting has notified the Ministry of Business Affairs that he is resigning from the Danish Financial Supervisory Authority’s board.” Citing unnamed sources, Danish financial news service FinansWatch reported that during the time between 2015 and 2018, when he was employed as head of security at Barclays bank, Ørting had been a key figure in the hunt for a whistleblower who had exposed the same criminal activity Ørting railed against at Cyber Polygon.

The man speaking alongside Ørting, Jürgen Stock, is a former German police officer, criminologist, and lawyer. He was elected for a second term as secretary general of INTERPOL in 2019, a term that generally lasts for five years. Craig Jones, the cybercrime director at INTERPOL, also joined the discussion at Cyber Polygon 2020. The New Zealander spent twenty-seven years in law enforcement and is considered an expert in cybercrime investigations. He previously held several senior-management positions in UK law enforcement, most recently at the National Crime Agency.
Petr Gorodov and John Crain were briefly interviewed at the Cyber Polygon 2020 event. Gorodov is head of the General Directorate for International Relations and Legal Assistance of the Prosecutor General’s Office of the Russian Federation and also sits on the Commission for the Control of INTERPOL’s files. He is on the Requests Chamber of INTERPOL, which examines and decides on requests for access to data as well as requests for correction and/or deletion of data processed in the INTERPOL information system. John Crain is chief security, stability, and resiliency officer at ICANN, the nonprofit internet security corporation. He is currently responsible for the management of the L-Root server, one of the internet’s thirteen root servers, making his inclusion at the simulation particularly notable. At Cyber Polygon 2020 he promoted a “long-term solution of working together in the cybersecurity community.”
The final word at Cyber Polygon 2020 was delivered by Stanislav Kuznetsov, deputy chairman of the executive board at Sberbank. He is also a board member for the Sberbank charity foundation Contribution to the Future, a project that seeks to get Russian schoolchildren from grades seven through eleven interested in AI (artificial intelligence), machine learning, and data analysis and to help them develop math and programming skills. Kuznetsov studied at the Law Institute of the Ministry of Internal Affairs of the Russian Federation.
The Main Event: Enter the Polygon
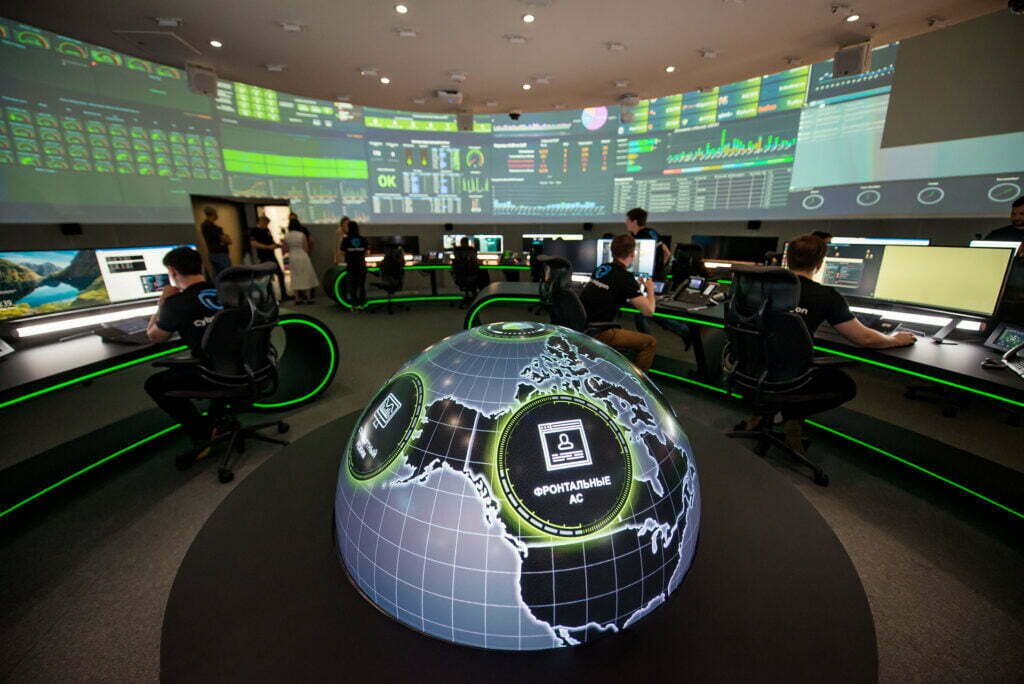

The simulation component of Cyber Polygon 2020 saw 120 teams from twenty-nine countries take part in the cybersecurity technical simulation. During the online event, participants “exercise[d] the actions of the response team in a targeted attack aimed at stealing confidential data and thus resulting in damage to the company reputation.” Two teams, the Red and the Blue, went head-to-head in the simulations where the Red Team, made up of the training organizers from BI.ZONE, simulated cyberattacks and the Blue Team members attempted to protect their segments of the training infrastructure. The actual simulation was made up of two scenarios in which the various subgroups making up the teams could gain points.
The first scenario, called Defence, made the Cyber Polygon participants practice repelling an active APT (advanced persistent threat) cyberattack. The scenario’s objective was stated as being to “develop skills for repelling targeted cyberattacks on a business-critical system.” The simulation’s fictional organization’s virtual infrastructure included a service that processes confidential client information. This service became the subject of interest to an APT group that planned to steal confidential user data and resell it on the “darknet” to financially benefit and damage the company’s reputation. The APT group studied the target system in advance and discovered several critical vulnerabilities. In the scenario, the cyber “gang” plans to attack on the day of the exercise. The participants involved were judged on their ability to cope with the attack as fast as possible, to minimize the amount of information stolen, and to maintain service availability. Blue Team participants could apply any applications and tools to protect the infrastructure and were also allowed to fix system vulnerabilities by improving the service code.
In the second scenario, called Response, the teams had to investigate the incident using “classic forensics and threat hunting techniques.” Based on the information gathered, participants had to compose a dossier that would help law enforcement agencies locate the criminals. The second scenario’s objective was to develop skills in incident investigation using the scenario in which cybercriminals gained access to a privileged account through a successful phishing attack.
When the BI.ZONE team released the results of the simulation they intentionally avoided using the real names of the organizations so as not to “set off a competition between the participants and keep their results confidential.” However, the teams could later compare their results with the others by using a basic scoreboard, and the hosts could analyse the crucial data showing various organizational weaknesses of each of the participating teams/institutions.
The final report states that the results showed that “banks and companies from the IT industry demonstrated the highest resilience. Security assessment expertise in these sectors is quite well developed, with classic forensics and threat hunting widely applied.” In lay terms, the teams from banks and the IT industry seemed to be better prepared than most other sectors for investigating and hunting down threats. However, all the teams involved proved to be less than able when it came to the initial defense from a cyberattack, with the BI.ZONE report stating that “27% of the teams had difficulties earning points for the first scenario, which allows us to conclude that some of the team members lack or have insufficient expertise in security assessment and protection of web applications.” On the subject of threat hunting, the report goes on to say that “21% of the teams could not earn a single point for the second round of the second scenario. This was attributed to ‘Threat Hunting’ being a relatively novel approach and the majority of organisations lacking experience of applying its techniques in practice.”
The Cyber Polygon 2020 event revealed the weakness in human-led defensive response and resilience as it relates cyberdefense. This outcome is convenient for hi-tech cybersecurity companies like BI.ZONE that wish to highlight the superiority of AI-driven cybersecurity products in comparison to “inefficient” human workers. Also, it should be noted that BI.ZONE’s gaining knowledge of global institutional weaknesses through cyberdefense training could be useful intelligence for their parent company, Sberbank, and in turn the largest shareholder of Sberbank, the Russian government.
Bringing Russia in from the Cold?
Although Russian Federation authorities are quite used to being out in the cold both politically and physically, there appears to be a change in the usual order of nations. Russia’s inclusion as the leader in such an important global cybersecurity initiative is a bit surprising, especially after Russia has been the scapegoat of choice for any cyberattack committed against any Western power for several years, most recently with the SolarWinds hack in the US. Yet, there was no outcry in the West over Cyber Polygon 2020, in which a company that is majority owned by the Russian government was able to gain direct knowledge of the cyberdefense weaknesses of major global institutions, banks, and corporations through their hosting of the exercise.
The complete absence of the “Russian hacker” narrative at Cyber Polygon as well as Russia’s leadership role at the event suggests either that a geopolitical shift has taken place or that the Russian hacker narrative commonly deployed by intelligence agencies in the US and Europe is mainly meant for the general public and not for the elite figures and policymakers in attendance at Cyber Polygon.
Another possibility for Russia no longer being treated as the perpetual enemy of cyberspace is that it is entirely on board with both the official coronavirus narrative and the allegedly imminent cyberpandemic. Cyber Polygon 2020 appeared, in part, to be a Russian charm offensive that was welcomed by the powerful elite. Tony Blair, who once held out the hand of false reconciliation on behalf of the international community to Colonel Gaddafi, has often been involved in these exercises of international diplomacy on behalf of the elites in the years since he left public office. His involvement in the exercise may have been meant to facilitate support among Western WEF-aligned governments for even greater Russian inclusion in the Great Reset. Part of this is due to the WEF-led effort to bring BRICS nations like China and Russia into the Great Reset fold because it is essential for their agenda’s success on a global scale. Now, Russia is pioneering this new model of supposedly national finance systems that the WEF supports through Sberbank’s creation of a digital monopoly not only of financial services but all services within the Russian Federation.
Cyber Polygon 2020 was both an ad for pro-Russian relations and a promotional exercise for Klaus Schwab and the World Economic Forum’s Great Reset. Some of the people who took part and supported the Cyber Polygon event are involved at the highest levels of cyber intelligence; some may have even been unofficial representatives of their national state intelligence apparatus. The decisions of several national governments to participate directly in the WEF-led Great Reset is no “conspiracy theory.” For instance, the incoming Biden administration sent its climate envoy, John Kerry, to the WEF annual meeting last month, where Kerry underscored the US commitment to the Great Reset agenda and the associated Fourth Industrial Revolution that seeks to automate most jobs being currently performed by humans. With the governments of Russia, China, the US, the UK, Israel, Canada, and India, among others, on board with this transnational agenda, it becomes deeply unsettling that high-ranking operatives in both the public and private sectors joined the WEF to conduct a simulation of a crisis that would clearly benefit the Great Reset agenda.
As previously mentioned, the WEF cosponsored a simulation of a coronavirus pandemic just months before the actual event. Soon after the COVID-19 crisis began in earnest last March, Schwab noted that the pandemic crisis was just what was needed to launch the Great Reset as it served as a convenient catalyst to begin overhauling economies, governance, and social society on a global scale. If the destabilizing events simulated at Cyber Polygon do come to pass, it will likely be similarly welcomed by the WEF, given that a critical failure in the current global financial system would allow the introduction of new public-private “digital ecosystem” monopolies such as those being built in Russia by Sberbank.
This effort by Sberbank to both digitize and monopolize access to all services, both private and public, may be appealing to some because of its apparent convenience. However, it will also be emblematic of what we can expect from Schwab’s Great Reset—monopolies of fused public- and private-sector entities disguised by the term “stakeholder capitalism.” What the general public does not realize yet is that they themselves will not be included among these “stakeholders,” as the Great Reset has been designed by the bankers and wealthy elite for the bankers and the wealthy elite.
As for the Cyber Polygon 2020 event, the coming cyberpandemic is being prophetically thrown in our faces just as the pandemic exercise was prior to the actual disease’s appearance. Such prophetic warnings are coming not only from the WEF, however. For instance, the head of Israel’s National Cyber Directorate, Yigal Unna, warned last year that a “cyber winter” of cyberattacks “is coming and coming faster than even I suspected.” In the cyber directorate, Unna works closely with Israeli intelligence agencies, including the infamous Unit 8200, which has a long history of electronic espionage targeting the US and other countries and which has been responsible for several devastating hacks, including the Stuxnet virus that damaged Iran’s nuclear program. Israeli intelligence is also poised to be among the greatest beneficiaries of the Great Reset due to the strength of the nation’s hi-tech sector. In addition, last month saw the UAE’s central bank following Cyber Polygon’s lead by conducting its first-ever cyberattack simulation in coordination with the Emirati private-finance sector. Corporate media outlets, for their part, began this year by claiming that “cyberattacks may trigger the next crisis for banks” and, as of February 1, that “the next cyberattack is already underway.”
Some will say that a “cyberpandemic” is an inevitable consequence of the quickly developing hi-tech world in which we live, but it still fair to point out that 2021 is the year that many have been predicting for the financial destruction of big institutions that will lead to new economic systems that align with the Great Reset. The inevitable collapse of the global banking system, resulting from the off-the-charts corruption and fraud that has run rampant for decades, is likely to be conducted through a controlled collapse, one that would allow wealthy bankers and elites, such as those that participated in Cyber Polygon, to avoid responsibility for their economic pillaging and criminal activity.
This is especially true for Cyber Polygon participant Deutsche Bank, whose inevitable collapse has been openly discussed for years due to the bank’s extreme corruption, fraud, and massive exposure to derivatives. In late 2019, months before the COVID-19 crisis began, the CEO of Deutsche Bank warned that central banks no longer had tools that could adequately respond to the next “economic crisis.” It is certainly telling that entirely new banking systems, such as Sberbank’s soon-to-be-launched digital monetary monopoly, began to be developed just as it began to be publicly acknowledged that central banks’ traditional means of responding to economic calamities were no longer viable.
A massive cyberattack, such as that simulated at Cyber Polygon 2020, would allow faceless hackers to be blamed for economic collapse, thus absolving the real financial criminals of responsibility. Furthermore, due to the difficult nature of investigating hacks and the ability of intelligence agencies to frame other nation states for hacks they in fact committed themselves, any boogeyman of choice can be blamed, whether a “domestic terror” group or a country unaligned with the WEF (for now, at least) like Iran or North Korea. Between the well-placed warnings, simulations, and the clear benefit for the global elite intent on a Great Reset, Cyber Polygon 2020 appears to have served not only its publicly stated purpose but its own ulterior motives.