This article was originally published on MintPress News.
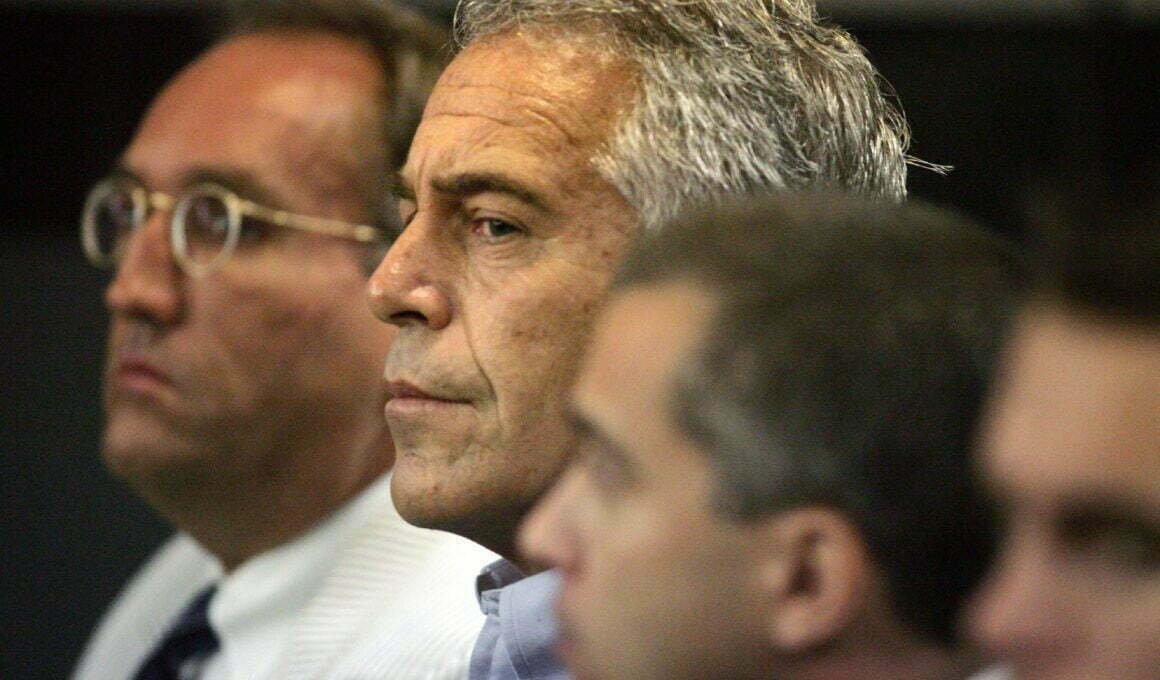
Despite his “sweetheart” deal and having seemingly evaded justice, billionaire sex offender Jeffrey Epstein was arrested earlier this month on federal charges for sex trafficking minors. Epstein’s arrest has again brought increased media attention to many of his famous friends, the current president among them.
Many questions have since been asked about how much Epstein’s famous friends knew of his activities and exactly what Epstein was up to. The latter arguably received the most attention after it was reported that Alex Acosta — who arranged Epstein’s “sweetheart” deal in 2008 and who recently resigned as Donald Trump’s Labor Secretary following Epstein’s arrest — claimed that the mysterious billionaire had worked for “intelligence.”
Other investigations have made it increasingly clear that Epstein was running a blackmail operation, as he had bugged the venues — whether at his New York mansion or Caribbean island getaway — with microphones and cameras to record the salacious interactions that transpired between his guests and the underage girls that Epstein exploited. Epstein appeared to have stored much of that blackmail in a safe on his private island.
Claims of Epstein’s links and his involvement in a sophisticated, well-funded sexual blackmail operation have, surprisingly, spurred few media outlets to examine the history of intelligence agencies both in the U.S. and abroad conducting similar sexual blackmail operations, many of which also involved underage prostitutes.
In the U.S. alone, the CIA operated numerous sexual blackmail operations throughout the country, employing prostitutes to target foreign diplomats in what the Washington Post once nicknamed the CIA’s “love traps.” If one goes even farther back into the U.S. historical record it becomes apparent that these tactics and their use against powerful political and influential figures significantly predate the CIA and even its precursor, the Office of Strategic Services (OSS). In fact, they were pioneered years earlier by none other than the American Mafia.
In the course of this investigation, MintPress discovered that a handful of figures who were influential in American organized crime during and after Prohibition were directly engaged in sexual blackmail operations that they used for their own, often dark, purposes.
In Part I of this exclusive investigation, MintPress will examine how a mob-linked businessman with deep ties to notorious gangster Meyer Lansky developed close ties with the Federal Bureau of Investigation (FBI) while also running a sexual blackmail operation for decades, which later became a covert part of the anti-communist crusade of the 1950s led by Senator Joseph McCarthy (R-WI), himself known throughout Washington for having a habit of drunkenly groping underage teenaged girls.
Yet, it would be one of McCarthy’s closest aides who would take over the ring in later years, trafficking minors and expanding this sexual blackmail operation at the same time he expanded his own political influence, putting him in close contact with prominent figures including former President Ronald Reagan and a man who would later become president, Donald Trump.
As will be revealed in Part II, after this figure’s death, the blackmail operation continued under various successors in different cities and there is strong evidence that Jeffrey Epstein became one of them.
Samuel Bronfman and the Mob
The Prohibition Era in the United States is often used as an example of how banning recreational substances not only increases their popularity but also causes a boom in criminal activity. Indeed, it was Prohibition that greatly increased the strength of the American Mafia, as the top crime lords of the day grew rich through the clandestine trade and sale of alcohol in addition to gambling and other activities.
It is through the bootlegging trade of the 1920s and the early 1930s that this story begins, as it brought together key figures whose successors and affiliates would eventually create a series of blackmail and sex trafficking rings that would give rise to the likes of Jeffrey Epstein, the “Lolita Express” and “Orgy Island.”
Samuel Bronfman never planned to become a major producer of liquor but true to his family’s last name, which means “brandy man” in Yiddish, he eventually began distributing alcohol as an extension of his family’s hotel business. During Canada’s Prohibition period, which was briefer than and preceded that of its southern neighbor, the Bronfman family business used loopholes to skirt the law and find technically legal ways to sell alcohol in the hotels and stores the family owned. The family relied on its connections with members of the American Mafia to illegally smuggle alcohol from the United States.
Soon after Prohibition ended in Canada, it began in the United States and, by the time the flow of illegal alcohol had turned the other way, the Bronfmans – whose business ventures were then being led by Sam Bronfman and his brothers — were relatively late to an already flourishing bootlegging trade.
“We were late starters in the two most lucrative markets – on the high seas and across the Detroit River. What came out of the border trade in Saskatchewan was insignificant by comparison,” Bronfman once told Canadian journalist Terence Robertson, who was then writing a biography of Bronfman. Nonetheless, “this was when we started to make our real money,” Bronfman recounted. Robertson’s biography on Bronfman was never published, as he died under mysterious circumstances soon after warning his colleagues that he had uncovered unsavory information about the Bronfman family.
Key to Bronfman’s success during American Prohibition were the ties his family had cultivated with organized crime during Canada’s Prohibition, ties that led many prominent members of the mob in the United States to favor Bronfman as a business partner. Bronfman liquor was purchased in massive quantities by many crime lords who still live on in American legend, including Charles “Lucky” Luciano, Moe Dalitz, Abner “Longy” Zwillman and Meyer Lansky.
Most of Bronfman’s mob associates during Prohibition were members of what became known as the National Crime Syndicate, which a 1950s Senate investigative body known as the Kefauver Committee described as a confederation dominated by Italian-American and Jewish-American mobs. During that investigation, some of the biggest names in the American Mafia named Bronfman as a central figure in their bootlegging operations. The widow of notorious American mob boss Meyer Lansky even recounted how Bronfman had thrown lavish dinner parties for her husband.
Years later, Samuel Bronfman’s children and grandchildren, their family’s ties to the criminal underworld intact, would go on to associate closely with Leslie Wexner, allegedly the source of much of Epstein’s mysterious wealth, and other mob-linked “philanthropists,” and some would even manage their own sexual blackmail operations, including the recently busted blackmail-based “sex cult” NXIVM. The later generations of the Bronfman family, particularly Samuel Bronfman’s sons Edgar and Charles, will be discussed in greater detail in Part II of this report.
Lewis Rosenstiel’s dark secret
Crucial to Bronfman’s Prohibition-era bootlegging operations were two middlemen, one of whom was Lewis “Lew” Rosenstiel. Rosenstiel got his start working at his uncle’s distillery in Kentucky before Prohibition. Once the law banning alcohol was in force, Rosenstiel created the Schenley Products Company, which would later become one of the largest liquor companies in North America.
Though he was a high school drop-out and not particularly well-connected socially at the time, Rosenstiel happened to have a “chance” meeting with Winston Churchill in 1922 while on vacation in the French Riviera. According to the New York Times, Churchill “advised him [Rosenstiel] to prepare for the return of liquor sales in the United States.” Rosenstiel somehow managed to secure the funding of the elite and respected Wall Street firm Lehman Brothers to finance his purchase of shuttered distilleries.
Officially, Rosenstiel is said to have built his company and wealth after Prohibition, by following Churchill’s advice to prepare for Repeal. However, he was clearly involved in bootlegging operations and was even indicted for bootlegging in 1929, though he evaded conviction. Like Bronfman, Rosenstiel was close to organized crime, particularly members of the mostly Jewish-American and Italian-American mob alliance known as the National Crime Syndicate.
Subsequent New York state legislative investigations would allege that Rosenstiel “was part of a ‘consortium’ with underworld figures that bought liquor in Canada [from Samuel Bronfman]”, whose other members were “Meyer Lansky, the reputed organized crime leader; Joseph Fusco, an associate of late Chicago gangster Al Capone and Joseph Linsey, a Boston man Mr. Kelly [the congressional investigator testifying] identified as a convicted bootlegger.” Rosenstiel’s relationship with these men, particularly Lansky, would continue long after Prohibition and Samuel Bronfman, for his part, would also maintain his mob ties.
In addition to his friends in the mob, Rosenstiel also cultivated close ties with the FBI, developing a close relationship with longtime FBI Director J. Edgar Hoover and making Hoover’s right-hand man and longtime assistant at the FBI, Louis Nichols, the Vice President of his Schenley empire in 1957.
Despite their similar backgrounds as bootlegger barons turned “respectable” businessmen, Bronfman’s and Rosenstiel’s personalities were drastically different and their relationship was complicated, at best. One example of the dissimilarities between North America’s top liquor barons was how they treated their staff. Bronfman was not necessarily known for being a cruel boss, whereas Rosenstiel was known for his erratic and “monstrous” behavior towards employees as well as his unusual practice of bugging his offices in order to hear what employees said about him when he wasn’t present.
Such differences between Bronfman and Rosenstiel were also reflected in their personal lives. While Bronfman married only once and was loyal to his wife, Rosenstiel was married five times and was known for his relatively closeted bisexual antics, a part of his life that was well-known to many of his close associates and employees.
Though for years there were only hints to this other side of the controversial businessman, details emerged years later during a divorce proceeding brought by Rosenstiel’s fourth wife, Susan Kaufman, that would back the claims. Kaufman alleged that Rosenstiel hosted extravagant parties that included “boy prostitutes” that her husband had hired “for the enjoyment” of certain guests, which included important government officials and prominent figures in America’s criminal underworld. Kaufman would later make the same claims under oath during the hearing of the New York’s State Joint Legislative Committee on Crime in the early 1970s.
Not only did Rosenstiel organize these parties, but he also made sure that their venues were bugged with microphones that recorded the antics of his high-profile guests. Those audio recordings, Kaufman alleged, were then kept for the purpose of blackmail. Though Kaufman’s claims are shocking, her testimony was deemed credible and held in high regard by the former chief counsel of the Crime Committee, New York Judge Edward McLaughlin, and committee investigator William Gallinaro and aspects of her testimony were later corroborated by two separate witnesses who were unknown to Kaufman.
These “blackmail parties” offer a window into an operation that would later become more sophisticated and grow dramatically in the 1950s under Rosenstiel’s “field commander” (a nickname given by Rosenstiel to an individual to be named shortly in this report). Many of the people connected to Rosenstiel’s “field commander” during the 70s and 80s have again found their names in the press following the recent arrest of Jeffrey Epstein.
The “Untouchable” Mobster
Bronfman and Rosenstiel became legendary in the North American liquor business, in part due to their fight for supremacy in the industry, which the New York Times described as often erupting “into bitter personal and corporate battles.” Despite their dueling in the corporate world, the one thing that united the two businessmen more than anything else was their close connection to American organized crime, particularly renowned mobster Meyer Lansky.
Lansky is one of the most notorious gangsters in the history of American organized crime and is notable for being the only famous mobster rising tonotoriety in the 1920s who managed to die an old man and never serve a day in jail.
Lansky’s long life and ability to avoid prison time was largely the result of his close relationships to powerful businessmen like Bronfman and Rosenstiel (among many others), the Federal Bureau of Investigation (FBI) and the U.S. intelligence community, as well as his role in establishing several blackmail and extortion rings that helped him keep the law at arm’s length. Indeed, when Lansky was finally charged with a crime in the 1970s, it was the Internal Revenue Service that brought the charges, not the FBI, and he was charged with and acquitted of tax evasion.
Lansky was remarkably close to both Bronfman and Rosenstiel. Bronfman regularly threw “lavish dinner parties” in Lansky’s honor both during and after Prohibition. These parties were remembered fondly by Lansky’s wife, and Lansky in turn did favors for Bronfman, ranging from exclusive protection of his shipments during Prohibition to getting him tickets to coveted “fight of the century” boxing matches.
Rosenstiel also threw regular dinner parties honoring Lansky. Susan Kaufman, Rosenstiel’s ex-wife, claimed to have taken numerous pictures of her ex-husband and Lansky socializing and partying together, photos that were also seen by Mary Nichols of The Philadelphia Inquirer. In addition, Lansky, per Kaufman’s recollection, was one of the individuals that Rosenstiel sought to protect from legal scrutiny as part of his child prostitution and blackmail ring targeting high-ranking officials, and he was overheard saying that if the government “ever brings pressure against Lansky or any of us, we’ll use this [a specific recording taken at one of the ‘parties’] as blackmail.”
Lansky was known to address Rosenstiel as “Supreme Commander,” a title that would later be used to refer to Rosenstiel by another individual deeply connected to the mob and sexual blackmail operations, previously referred to in this report as Rosenstiel’s “Field Commander.”
Lansky also had close ties to the CIA and U.S. military intelligence. During World War II, Lansky — along with his associate Benjamin “Bugsy” Siegel — worked with Naval intelligence in what was codenamed “Operation Underworld,” an operation the existence of which the government denied for over 40 years.
Journalist and noted chronicler of CIA covert activities, Douglas Valentine, noted in his book The CIA as Organized Crime: How Illegal Operations Corrupt America and the World that the government’s cooperation with the Mafia during World War II led to its expansion after the war and set the stage for its future collaboration with U.S. intelligence.
According to Valentine:
Top government officials were also aware that the government’s Faustian pact with the Mafia during World War II had allowed the hoods to insinuate themselves into mainstream America. In return for services rendered during the war, Mafia bosses were protected from prosecution for dozens of unsolved murders. […]
The Mafia was a huge problem in 1951 [when the Kefauver Committee was convened], equivalent to terrorism today. But it was also a protected branch of the CIA, which was co-opting criminal organizations around the world and using them in its secret war against the Soviets and Red Chinese. The Mafia had collaborated with Uncle Sam and had emerged from World War II energized and empowered. They controlled cities across the country.”
Indeed, not long after its creation, the CIA forged ties with Lansky at the behest of CIA counterintelligence chief James J. Angleton. The CIA would later turn to the Lansky-linked mob in the early 1960s as part of its consistently fruitless quest to assassinate Cuban leader Fidel Castro, showing that the CIA maintained its contacts with Lansky-controlled elements of the Mafia long after the initial meeting with Lansky took place.
The CIA also had close connections to associates of Lansky, such as Edward Moss, who did public relations work for Lansky and was said to be of “interest” to the CIA by the agency’s then-inspector general J.S. Earman. Harry “Happy” Meltzer was also another Lansky associate that was a CIA asset and the CIA asked Meltzer to join an assassination team in December 1960.
In addition to the CIA, Lansky was also connected to a foreign intelligence agency through Tibor Rosenbaum, an arms procurer and high-ranking official in Israel’s Mossad, whose bank – the International Credit Bank of Geneva –laundered much of Lansky’s ill-gotten gains and recycled them into legitimate American businesses.
Journalist Ed Reid, author of the Virginia Hill biography The Mistress and the Mafia, wrote that Lansky was attempting to entrap powerful people through sexual blackmail as far back as 1939. Reid contends that Lansky sent Ms. Hill to Mexico, where his West Coast connections had established a drug ring that later involved the OSS, the forerunner to the CIA, to seduce numerous “top politicians, army officers, diplomats and police officials.”
Eventually, Lansky was credited with obtaining compromising photos of FBI Director J. Edgar Hoover sometime in the 1940s, which showed “Hoover in some kind of gay situation”, according to a former Lansky associate, who also said that Lansky had often claimed, “I fixed that sonofabitch.” The photos showed Hoover engaged in sexual activity with his long-time friend, FBI Deputy Director Clyde Tolson.
At some point, these photos fell into the hands of CIA counterintelligence chief James J. Angleton, who later showed the photos to several other CIA officials, including John Weitz and Gordon Novel. Angleton was in charge of the CIA’s relationship with the FBI and Israel’s Mossad until he left the agency in 1972 and, as was recently mentioned, he was also in contact with Lansky.
Anthony Summers, former BBC journalist and author of Official and Confidential: The Secret Life of J. Edgar Hoover, has argued that it was not Lansky, but William Donovan, the director of the OSS, who obtained the original photos of Hoover and later shared them with Lansky.
Summers also stated that “To [gangster Frank] Costello and Lansky, the ability to corrupt politicians, policemen and judges was fundamental to Mafia operations. The way they found to deal with Hoover, according to several mob sources, involved his homosexuality.” This anecdote shows that Lanksy and the CIA maintained a covert relationship, which included, among other things, the sharing of blackmail material (i.e., “intelligence”).
It is also possible that Hoover was ensnared by the mob during one of Rosenstiel’s “blackmail parties,” at which Hoover sometimes found himself in attendance with prominent figures of the Mafia. Hoover was said to have worn women’s clothing at the some of the events and Meyer Lansky’s wife later said that her husband had photos of the former FBI director in drag. Furthermore, Hoover is on record showing an unusual concern in the FBI’s handling of Rosenstiel’s criminal links as early as 1939, the same year that his close associate Lansky was actively orchestrating the sexual blackmail of powerful political figures.
The blackmail acquired on Hoover and the mob’s possession of the evidence has been cited as a major factor in Hoover’s decades-long denial that nationwide networks of organized crime were a serious issue. Hoover asserted that it was a decentralized, local issue and therefore outside of the bureau’s jurisdiction. By the time Hoover finally acknowledged the existence of national organized crime networks in 1963, they were so entrenched in the U.S. establishment that they were untouchable.
Congressional crime consultant Ralph Salerno told Summers in 1993 that Hoover’s willful ignorance of organized crime for most of his career as FBI director “allowed organized crime to grow very strong in economic and political terms, so that it became a much bigger threat to the wellbeing of this country than it would have been if it had been addressed much sooner.”
J. Edgar Hoover: Blackmail Victim?
Most records place the beginning of Hoover’s relationship with Rosenstiel in the 1950s, the same decade when Susan Kaufman reported that Hoover was attending Rosenstiel’s blackmail parties. Rosenstiel’s FBI file, obtained by Anthony Summers, cites the first Rosenstiel meeting as taking place in 1956, though Summers notes that there is evidence that they had met much earlier. After requesting the meeting, Rosenstiel was granted a personal face-to-face with the director in a matter of hours. The FBI file on Rosenstiel also reveals that the liquor baron heavily lobbied Hoover to aid his business interests.
During that time, the salacious details of Hoover’s sex life were already known to the U.S. intelligence community and to the mob, and Hoover was aware that they knew of his closeted sexuality and penchant for women’s clothing. Yet, Hoover apparently seemed to embrace the very type of sexual blackmail operation that had compromised his private life, given that he was seen at many of Rosenstiel’s “blackmail parties” in the 1950s and 1960s, including at venues such as Rosenstiel’s personal home and later at Manhattan’s Plaza Hotel. Hoover’s penchant for dressing in drag was also described by two witnesses who were not connected to Susan Kaufman.
Soon after their first “official” meeting, the public relationship between the two men quickly flourished, with Hoover even sending Rosenstiel flowers when he fell ill. Summers reported that, in 1957, Rosenstiel was heard telling Hoover during a meeting, “your wish is my command.” Their relationship remained close and intimate throughout the 1960s and beyond.
Like Rosenstiel, Hoover was well-known for amassing blackmail on friend and foe alike. Hoover’s office contained “secret files” on numerous powerful people in Washington and beyond, files he used to gain favors and protect his status as FBI director for as long as he wished.
Hoover’s own propensity for blackmail suggests that he may have associated with Rosenstiel’s sexual blackmail operation more directly, given he already knew he was compromised and his involvement in the operation would have served as a means of procuring the blackmail he coveted for his own purposes. Indeed, if Hoover was merely being blackmailed and extorted by the Lansky-Rosenstiel connected mob, it is unlikely that he would have been so friendly to Rosenstiel, Lansky and the other mobsters at these gatherings and participated in them with such regularity.
According to journalist and author Burton Hersh, Hoover was also tied to Sherman Kaminsky, who ran a sexual blackmail operation in New York involving young male prostitutes. That operation was busted and investigated in a 1966 extortion probe led by Manhattan District Attorney Frank Hogan, though the FBI quickly took over the investigation and photos of Hoover and Kaminsky together soon disappeared from the case file.
Hoover and Rosenstiel’s deep ties would continue to develop over the years, an example of which can be seen in Rosenstiel’s hiring of long-time Hoover aide Louis Nichols as the vice president of his Schenley liquor empire and Rosenstiel’s donation of over $1 million to the J. Edgar Hoover Foundation, which Nichols also ran at the time.
There is also more than one documented occasion wherein Hoover attempted to use blackmail to protect Rosenstiel and his “field commander,” none other than the infamous Roy Cohn, the other key figure in Rosenstiel’s sexual blackmail operation involving minors.
The Making of a Monster
Decades after his death, Roy Cohn remains a controversial figure in large part because of his close, personal relationship with current U.S. President Donald Trump. Yet reports on Cohn, both in recent and in past years, often miss the mark in their characterization of the man who became closely associated with the Reagan White House, the CIA, the FBI, organized crime and, incidentally, many of the figures who would later surround Jeffrey Epstein.
To understand the true nature of the man, it is essential to examine his rise to power in the early 1950s when, at just 23 years of age, he became a key figure in the high-profile trial of Soviet spies Ethel and Julius Rosenberg and later as the right-hand man of Senator Joseph McCarthy (R-WI).
Cohn’s dedication to anti-communist activities in the 1950s is allegedly what first endeared him to J. Edgar Hoover, whom he first met in 1952. During that meeting, as described by Hersh in Bobby and J. Edgar: The Historic Face-Off Between the Kennedys and J. Edgar Hoover That Transformed America, Hoover expressed admiration for Cohn’s aggressive and manipulative tactics and told Cohn to “call me directly” whenever he had information worth sharing. From that point on, Cohn and Hoover “traded favors, effusive compliments, gifts and elaborate private dinners. It quickly became ‘Roy’ and ‘Edgar.’” Hersh also describes Hoover as Cohn’s soon to be “consigliere.”
The date and circumstances around Cohn’s introduction to Rosenstiel are harder to come by. It is possible that the connection was made through Roy Cohn’s father, Albert Cohn, a prominent judge and an influential figure in the New York City Democratic Party apparatus then run by Edward Flynn. It was later revealed that the Democratic organization dominated by Flynn and based in the Bronx had long-standing connections to organized crime, including associates of Meyer Lansky.
Regardless of how or when it began, the relationship between Cohn and Rosenstiel was close and was often likened to that of a father and son. They were said to frequently salute each other in public and remained close until Rosenstiel was near death, at which point Cohn attempted to trick his then-barely conscious and senile “friend” and client into naming him the executor and trustee of the liquor magnate’s estate, valued at $75 million (more than $334 million in today’s dollars).
LIFE magazine reported in 1969 that Cohn and Rosenstiel had for years referred to one another as “Field Commander” and “Supreme Commander,” respectively. Media references to these nicknames appear in other articles from the period.
Though LIFE and other outlets had interpreted this as merely an anecdote about the nicknames shared in jest between close friends, the fact that notorious crime lord Meyer Lansky also called Rosenstiel “Supreme Commander” and the fact that Cohn and Rosenstiel would later become intimately involved in the same pedophile sex ring suggests that there may have been more to these “nicknames.” After all, the mob to which Rosenstiel was connected often used military-themed titles like “soldier” and “lieutenant” to differentiate the rank and importance of its members.
Once he had made his connection with Hoover, Cohn’s star began to rise even higher in Washington. Hoover’s recommendation of Cohn would become the deciding factor in his appointment as Sen. McCarthy’s general counsel over Robert Kennedy, a rival and bitter enemy of Cohn’s.
Though Cohn was ruthless and seemingly untouchable as McCarthy’s counsel and helped the senator destroy many careers during both the red and lavender scares, his antics in relation to his work on the committee would eventually lead to his downfall after he attempted to blackmail the Army in return for preferential treatment for committee consultant and Cohn’s rumored lover, David Schine.
After he was forced to leave McCarthy’s side due to the scandal, Cohn returned to New York to live with his mother and practice law. A few years later New York Judge David Peck, a long-time associate of former CIA Director Alan Dulles, orchestrated Cohn’s hire to the New York law firm Saxe, Bacon and O’Shea — which would later become Saxe, Bacon and Bolan after Tom Bolan, a friend of Cohn’s, became a partner in the firm. Upon his hire, Cohn brought the firm a slew of Mafia-linked clients, including high-ranking members of the Gambino crime family, the Genovese crime family and, of course, Lewis Rosenstiel.
What happened in Suite 233?
The connections Roy Cohn built during the 1950s made him a well-known public figure and translated into great political influence that peaked during the presidency of Ronald Reagan. Yet, as Cohn built his public image, he was also developing a dark private life, which would come to be dominated by the same blackmail pedophile racket that appears to have first begun with Lewis Rosenstiel.
One of the “blackmail parties” Susan Kaufman attended with her then-husband Lewis Rosenstiel was hosted by Cohn in 1958 at Manhattan’s Plaza Hotel, suite 233. Kaufman described Cohn’s suite as a “beautiful suite…all done in light blue.” She described being introduced to Hoover, who was in drag, by Cohn, who told her that Hoover’s name was “Mary” in a fit of barely concealed laughter. Kaufman testified that young boys were present and Kaufman claimed that Cohn, Hoover and her ex-husband engaged in sexual activity with these minors.
New York attorney John Klotz, tasked with investigating Cohn for a case well after Kaufman’s testimony, also found evidence of the “blue suite” at the Plaza Hotel and its role in a sex extortion ring after combing through local government documents and information gathered by private detectives. Klotz later told journalist and author Burton Hersh what he had learned:
Roy Cohn was providing protection. There were a bunch of pedophiles involved. That’s where Cohn got his power from — blackmail.”
Perhaps the most damning confirmation of Cohn’s activities in Suite 233 comes from statements made by Cohn himself to former NYPD detective and ex-head of the department’s Human-Trafficking and Vice-Related Crimes Division, James Rothstein. Rothstein later told John DeCamp — a former Nebraska state senator who investigated a government-connected child sex ring based in Omaha — among other investigators, that Cohn had admitted to being part of a sexual blackmail operation targeting politicians with child prostitutes during a sit-down interview with the former detective.
Rothstein told DeCamp the following about Cohn:
Cohn’s job was to run the little boys. Say you had an admiral, a general, a congressman, who did not want to go along with the program. Cohn’s job was to set them up, then they would go along. Cohn told me that himself.”
Rothstein later told Paul David Collins, a former journalist turned researcher, that Cohn had also identified this sexual blackmail operation as being part of the anti-communist crusade of the time.
The fact that Cohn, per Rothstein’s recollection, stated that the child sex blackmail ring was part of the government-sponsored anti-communist crusade suggests that elements of the government, including Hoover’s FBI, may have been connected at a much broader level than Hoover’s own personalinvolvement, as the FBI closely coordinated with McCarthy and Cohn for much of the red scare.
It is also worth noting that among Hoover’s many “secret” blackmail files was a sizeable dossier on Senator McCarthy, the contents of which strongly suggested that the senator himself was interested in underage girls. According to journalist and author David Talbot, Hoover’s file on McCarthy was “filled with disturbing stories about McCarthy’s habit of drunkenly groping young girls’ breasts and buttocks. The stories were so widespread that they became ‘common knowledge’ in the capital, according to one FBI chronicler.”
Talbot, in his book The Devil’s Chessboard, also cites Walter Trohan, Washington Bureau Chief of the Chicago Tribune, as having personally witnessed McCarthy’s habit of molesting young women. “He just couldn’t keep his hands off young girls,” Trohan would later say. “Why the Communist opposition didn’t plant a minor on him and raise the cry of statutory rape, I don’t know.” Perhaps the answer lies in the fact that those “planting” minors on their political foes were McCarthy’s allies and close associates, not his enemies.
The question that necessarily arises from revelations regarding Cohn’s activities in Suite 233 is who else was Cohn “protecting” and servicing with underage prostitutes? One of them could very well have been one of Cohn’s close friends and clients, Cardinal Francis Spellman of the Archdiocese of New York, who was said to have been present at some of these parties Cohn hosted at the Plaza Hotel.
Spellman — one of the most powerful figures in the Catholic Church in North America, who was sometimes referred to as “America’s Pope” — was accused of not only condoning pedophilia in the Catholic church and ordaining known pedophiles including Cardinal Theodore “Uncle Teddy” McCarrick, but also engaging in it himself to such an extent that many New York area priests widely referred to him as “Mary.” Furthermore, J. Edgar Hoover was said to have a file detailing the cardinal’s sex life, suggesting Spellman’s involvement in the ring and pedophile protection racket in which Cohn and Hoover were personally involved.
People close to Cohn often remarked that he was frequently surrounded by groups of young boys, but seemed to think nothing of it. Similar off-handed comments about Epstein’s penchant for minors were made by those close to him prior to his arrest.
Controversial Republican political operative and “dirty trickster” Roger Stone — who, like Donald Trump, was also a protégé of Cohn — said the following about Cohn’s sex life during an interview with The New Yorker in 2008:
Roy was not gay. He was a man who liked having sex with men. Gays were weak, effeminate. He always seemed to have these young blond boys around. It just wasn’t discussed. He was interested in power and access.” (emphasis added)
Compare this quote from Stone to what Donald Trump, who was also close to Cohn, would later say about Jeffrey Epstein, with whom he was also closely associated:
I’ve known Jeff for 15 years. Terrific guy. He’s a lot of fun to be with. It is even said that he likes beautiful women as much as I do, and many of them are on the younger side. No doubt about it — Jeffrey enjoys his social life.” (emphasis added)
Though it is unknown how long the sex ring at the Plaza Hotel continued, and whether it continued after Cohn’s death from AIDS in 1986, it is worth noting that Donald Trump purchased the Plaza Hotel in 1988. It would later be reported and confirmed by then-attendees that Trump “used to host parties in suites at the Plaza Hotel when he owned it, where young women and girls were introduced to older, richer men” and “illegal drugs and young women were passed around and used.”
Andy Lucchesi, a male model who had helped organize some of these Plaza Hotel parties for Trump, said the following when asked about the age of the women present: “A lot of girls, 14, look 24. That’s as juicy as I can get. I never asked how old they were; I just partook. I did partake in activities that would be controversial, too.”
The Roy Cohn Machine
Roy Cohn was only at the beginning of his career when he waded his way into the underground sexual blackmail ring apparently led by Lewis Rosenstiel. Indeed, when Cohn first met Hoover, he was only 23 years old. Over the next three decades or so, before his death from AIDS-related complications in 1986 at the age of 56, Cohn built a well-oiled machine, largely through his close friendships with some of the country’s most influential figures.
Among Cohn’s friends were top media personalities like Barbara Walters, former CIA directors, Ronald Reagan and wife Nancy, media moguls Rupert Murdoch and Mort Zuckerman, numerous celebrities, prominent lawyers like Alan Dershowitz, top figures in the Catholic Church and leading Jewish organizations like B’nai B’rith and the World Jewish Congress. Many of the same names that surrounded Cohn until death in the late 1980s would later come to surround Jeffrey Epstein, with their names later appearing in Epstein’s now-infamous “little black book”.
While President Trump is clearly connected to both Epstein and Cohn, Cohn’s network also extends to former President Bill Clinton, whose friend and longtime political advisor, Richard “Dirty Dick” Morris, was Cohn’s cousin and close associate. Morris was also close to Clinton’s former communications director, George Stephanopoulos, who is also associated with Jeffrey Epstein.
Yet, these were only Cohn’s connections to respectable members of the establishment. He was also known for his deep connections to the mob and gained prominence largely for his ability to connect key figures in the criminal underworld to respected influential figures acceptable to the public sphere. Ultimately, as New York attorney John Klotz stated, Cohn’s most powerful tool was blackmail, which he used against friend and foe, gangster or public official alike. How much of that blackmail he acquired through his sexual blackmail operation will likely never be known.
As Part II of this exclusive investigation will reveal, Cohn and Epstein, and the sexual blackmail operations they ran share many things in common, including not only many of the same famous friends and patrons, but also connections to intelligence agencies and consortiums of mob-linked businessmen, the modern-day equivalents of Samuel Bronfman and Lewis Rosenstiel who have since rebranded as “philanthropists.”
Part II will also reveal that Cohn’s operation was known to have successors, as revealed by a series of scandals in the early 1990s that have since been swept under the rug. The significant amount of overlap between Epstein’s and Cohn’s covert activities in sexual blackmail and their ties to many of the same powerful individuals and circles of influence strongly suggest that Epstein was one of Cohn’s successors.
As will be shown in the final installment of this report, Epstein is only the latest incarnation of a much older, more extensive and sophisticated operation that offers a frightening window into how deeply tied the U.S. government is to the modern-day equivalents of organized crime, making it a racket truly too big to fail.